Traditional legal systems have been developed over centuries to serve the needs of specific cultures and societies. These systems reflect the values, beliefs, and traditions of the communities that created them. However, as societies and cultures change, these legal systems may become outdated and no longer meet the needs of their people. To address this challenge, there is a growing movement to reimagine traditional legal systems for today’s world. This movement is driven by the recognition that there is value in preserving the wisdom and insights of the past while also adapting them to the needs of the present. In this article, we explore several traditional legal systems from different parts of the world and how they can inspire modern legal systems to become more effective, equitable, and sustainable.
Ubuntu:
Restoring Relationships and Promoting Interconnectedness in Africa
The African concept of Ubuntu emphasizes the interconnectedness of all individuals and prioritizes the restoration of relationships. This approach sees conflicts and disputes as a breakdown in relationships rather than as individual wrongdoing. Therefore, the resolution process aims to restore the relationship between the parties involved. This philosophy is deeply ingrained in African societies and has influenced many modern restorative justice programs around the world.

Ubuntu is not just a legal system, but a way of life that emphasizes the importance of community, respect, and compassion. The Ubuntu philosophy encourages individuals to prioritize the well-being of their communities over their own self-interests. This approach to justice involves bringing all parties involved in a dispute together to discuss the harm caused and work toward a resolution that will restore the relationship and promote healing.
This process is often facilitated by a mediator or peacemaker who helps guide the conversation and encourages each party to listen and understand the other’s perspective. Ubuntu’s focus on restoring relationships has proven to be a successful approach to resolving conflicts in various contexts, including criminal justice, family disputes, and community conflicts. By prioritizing interconnectedness and community well-being, Ubuntu offers a unique and powerful alternative to traditional legal systems.
Circle-Based Peacemaking:
Dispute Resolution Among the Navajo Nation
The Navajo Nation’s peacemaking process is a circle-based approach that brings together all parties involved in a dispute to work toward a resolution. The process is designed to be collaborative, and the mediator encourages open communication and dialogue between the parties. The circle-based approach is based on the Navajo philosophy that everything in the universe is connected, and harmony can be achieved through respectful communication.

The Navajo Nation’s peacemaking process is a circle-based approach that brings together all parties involved in a dispute to work toward a resolution. The process is designed to be collaborative, and the mediator encourages open communication and dialogue between the parties. The circle-based approach is based on the Navajo philosophy that everything in the universe is connected, and harmony can be achieved through respectful communication.
The peacemaking process is deeply rooted in Navajo culture and tradition, and it is based on the concept of “K’e,” which means kinship or relationship. According to the Navajo belief, all things are connected and have a spiritual essence. Therefore, relationships and harmony are essential to maintain balance and well-being. The circle-based approach is a physical representation of this concept, with all parties seated in a circle to show that everyone is equal and interconnected.

During the process, the mediator encourages participants to share their perspectives and emotions, and actively listens to each person’s story. This approach helps to build trust and understanding between the parties, and fosters a sense of community and belonging. The mediator then works with the parties to find a mutually acceptable solution that promotes harmony and restores relationships.
Overall, the Navajo peacemaking process is a unique and powerful approach to conflict resolution that prioritizes communication, respect, and community involvement. Its success is a testament to the importance of cultural values and traditions in shaping effective legal systems.
Koseki:
Family Registry System in Japan
The Koseki system is a family registry system that has been used in Japan since the 1800s. It provides a comprehensive record of all family members and their relationships. This system is considered one of the oldest and most reliable forms of identification in Japan. In fact, the Koseki system is so ingrained in Japanese culture that it is often used as a standard reference for verifying personal identity in everyday life, from opening a bank account to getting a driver’s license.
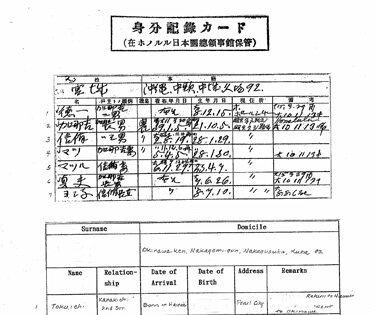
The Koseki system is not just a tool for tracking genealogy, but it also serves as a legal framework for family relationships. This system is designed to promote family stability and has been credited with helping to reduce the incidence of child abandonment and illegitimacy. The Koseki system also plays an important role in Japanese inheritance laws, as it provides a clear record of family lineage and helps ensure that property is passed down to the appropriate family members. Overall, the Koseki system has been a crucial part of Japanese family life for generations.
Tinku:
Community Involvement in Dispute Resolution
The Tinku system of justice in the Inca civilization was a unique way of resolving conflicts that involved physical fights. The Tinku fights were not just about physical combat, but rather an opportunity for disputing parties to come together and reach a mutual understanding. These fights were typically held in a public square, where people from the surrounding communities would gather to watch. The fights were often accompanied by music, dance, and celebrations, creating a festive atmosphere.

The Inca system of justice also emphasized community involvement in dispute resolution. Elders and respected members of the community would often mediate between the parties involved in a dispute. This was done to ensure that the resolution was fair and just, and that all parties were satisfied with the outcome. The Inca people believed that by involving the community in the resolution process, they could maintain social harmony and prevent future conflicts from arising. This approach to justice is still studied and admired today for its focus on community involvement and peaceful conflict resolution.
The Great Law of Peace:
The Iroquois Confederacy’s Council-Based Decision-Making
The Iroquois Confederacy’s Great Law of Peace is not only a legal system but also a political and social organization that values the importance of maintaining good relationships among its members. The Great Law of Peace aims to establish a peaceful and harmonious society by upholding principles such as respect, unity, and equality. One of the unique features of this legal system is the use of consensus-based decision-making. Every member of the community has a voice and a vote in the decision-making process, and the goal is to reach an agreement that benefits everyone.
The Great Law of Peace also includes a set of laws that outline the rights and responsibilities of individuals within the community. The laws cover a wide range of topics, including property rights, environmental protection, and criminal justice. The system is designed to prevent disputes and conflicts by addressing issues before they escalate into major problems. The Great Law of Peace has been influential in the development of other legal systems that prioritize community involvement in decision-making and conflict resolution.
Ancient Harmony and Social Stability:
Old and Modern Approaches to Law in the Chinese Legal System:
The Chinese legal system, with its long and complex history, has evolved over time to emphasize the importance of social harmony and stability over individual rights. The Chinese legal system has a long history that dates back to ancient China. One of the earliest legal codes was the Tang Code, which was established in the 7th century. Throughout Chinese history, the legal system has been influenced by Confucianism and Taoism, which emphasized social order, morality, and respect for authority.
One of the key aspects of this system is the focus on mediation and conciliation, which are seen as more effective means of resolving disputes than punishment. Mediation is encouraged in all areas of life, including business and family disputes, and is often conducted by a neutral third party. This approach is based on the Chinese concept of “guanxi,” which emphasizes the importance of relationships and social networks in Chinese society.

In addition to mediation, the Chinese legal system also places a strong emphasis on prevention. Laws and regulations are put in place to prevent conflicts from occurring in the first place, and the system also encourages individuals to take responsibility for their actions and behave in a way that is harmonious with society. Punishment is seen as a last resort, and even then, the emphasis is on rehabilitating the offender and restoring social harmony. This approach has been credited with promoting social stability and preventing conflicts from escalating into larger-scale societal problems.
Today, the legal system of modern China is vastly different from its historical predecessors, with the Communist Party of China (CCP) playing a dominant role in shaping the legal framework. Since the establishment of the People’s Republic of China in 1949, the legal system has undergone significant changes, including the adoption of a socialist legal system that reflects Marxist ideology. The CCP has also been criticized for using the legal system to suppress dissent and maintain its grip on power. Despite these changes, there are still some aspects of traditional Chinese legal principles that continue to be relevant in the modern legal system.
Dharma:
Moral Duty and Ethical Responsibility in India
Dharma, which is derived from ancient Indian texts, is a complex concept that encompasses many different meanings, including law, religion, and morality. In the context of decision-making and dispute resolution, dharma emphasizes the importance of upholding one’s moral duty and ethical responsibility to society. This approach sees conflicts and disputes as a breakdown in the social order, and the resolution process aims to restore balance and harmony to the community.

One example of dharma in action is the panchayat system, which is a traditional form of community-based dispute resolution in rural India. The panchayat system brings together community members to discuss and resolve disputes through dialogue and mediation. The system is based on the principles of dharma and seeks to restore harmony and balance within the community by promoting mutual understanding and respect.
Moreover, the concept of dharma has also influenced modern Indian law, with the Indian constitution emphasizing the importance of justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity. The legal system in India is based on the principles of dharma, and the courts aim to resolve disputes in a fair and just manner that upholds the moral duty and ethical responsibility of all parties involved.
Cherokee Court:
Using Traditional Cherokee Values and Practices in Dispute Resolution
The Cherokee Nation’s court system is unique in its incorporation of traditional Cherokee values and practices into its legal framework. At the core of this system is a focus on rehabilitation and healing, rather than punishment. This approach is deeply rooted in the Cherokee concept of “gadugi,” which emphasizes the importance of community involvement in decision-making and conflict resolution.

The Cherokee Nation’s court system recognizes that crime and conflict not only harm individuals but also the entire community. As such, their approach to justice is aimed at repairing harm and restoring relationships. They achieve this through a system of alternative sentencing options that prioritize rehabilitation, such as community service, drug and alcohol treatment, and counseling. By providing resources for healing, rather than just punishment, the Cherokee Nation’s court system aims to address the root causes of crime and prevent recidivism.

Overall, the Cherokee Nation’s court system represents a model of justice that prioritizes healing and rehabilitation while recognizing the importance of community involvement in conflict resolution. This approach stands in contrast to the punitive model of justice that dominates many Western legal systems, which often perpetuates cycles of harm and fails to address the root causes of crime.
Compensation over Punishment
The Early Icelandic System of Mediation and Government
The Icelandic system of justice, which dates back to the Viking era, is another traditional legal system that is worth examining. Unlike many other systems that focused on punishment and retribution, the Icelandic system emphasized the importance of mediation and compensation in resolving disputes.

In the Icelandic system, disputes were typically resolved through a process known as “the law,” which involved a mediator who would hear the case and facilitate a resolution between the parties involved. If the parties were unable to reach a resolution through this process, they could take the case to a court made up of 36 judges who would then make a ruling.
The emphasis on compensation in the Icelandic system meant that offenders were required to make amends for their actions by paying fines or providing other forms of restitution to the victim. This focus on repairing harm and restoring relationships is similar to the principles of restorative justice, which is gaining popularity in modern legal systems around the world.

The Brehon Laws:
Ireland’s Ancient Poetic Legal Code
Brehon Law, also known as Fenechas, is a traditional legal system of Ireland that dates back to the pre-Christian era. This system was used by the ancient Irish to govern their society and regulate social behavior. Brehon Law emphasized the importance of fairness, equity, and balance in decision-making and conflict resolution, and it was based on the principle that every member of society had a responsibility to uphold the law.

Similar to other traditional legal systems, Brehon Law focused on restorative justice and alternative dispute resolution rather than punishment. It encouraged parties involved in a dispute to come to an agreement through negotiation and mediation, with the goal of restoring relationships and maintaining social harmony. The Brehon Law system was unique in that it did not have a central authority or governing body but relied on local judges and lawyers, called Brehons, to interpret and apply the law.
Today, there is a renewed interest in the Brehon Law system, and efforts are being made to incorporate its principles into modern legal systems. The Brehon Academy has contributed to these efforts since its founding in 2013. The Irish government has established a Brehon Law Project to research and promote the system, and there is a growing movement to use Brehon Law as a model for restorative justice in contemporary Ireland.
The Iroquois Confederacy’s Great Law of Peace and the Navajo Nation’s peacemaking process both prioritize collaborative decision-making and community involvement in dispute resolution. The Inca system of justice, Tinku, also emphasized community involvement in dispute resolution, but through physical fights rather than mediation. The Japanese Koseki system, on the other hand, focused on promoting family stability and providing a legal framework for family relationships. Comparing Brehon Law to other traditional legal systems, we see similarities in their emphasis on community involvement and restorative justice.

Incorporating principles from traditional legal systems like Brehon Law into modern justice systems could lead to more effective and equitable approaches to conflict resolution. By emphasizing restorative justice and alternative dispute resolution, rather than punishment, we can create a more just and harmonious society.
These traditional legal systems offer valuable insights into different approaches to justice and conflict resolution. They emphasize community involvement, restoration of relationships, and moral responsibility, all of which can be useful in modern justice systems. These approaches prioritize finding peaceful solutions to disputes over punishment or retribution, which can help build stronger and more cohesive societies. By learning from and adapting these traditional legal systems to meet the needs of today’s world, we can create more effective, equitable, and just systems of conflict resolution that prioritize harmony and social stability.






